Study shows clear influence of driving noise on individual sound preferences in a car
More than just loud bass!
Loud or unpleasant driving noises can impair the enjoyment of music in the car. Some sound systems therefore dynamically adjust the volume and bass. However, individual sound preferences are not taken into account. A study from Fraunhofer IDMT in Oldenburg has now investigated the influence of background noise on the personal sound experience while driving – and shows how an adjustment of individual sound preferences once could improve the sound in the vehicle (and beyond).
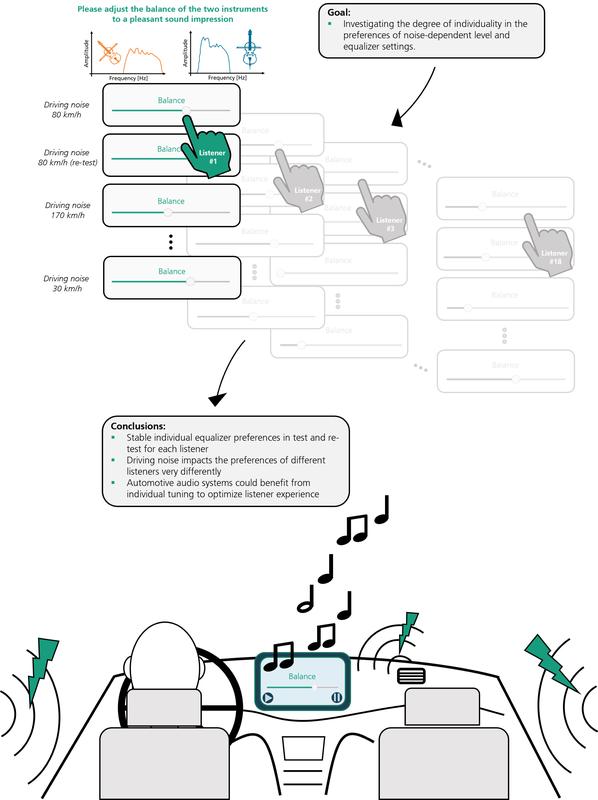
Oldenburg, 23 July 2024. For over 15 years, the Personalized Hearing Systems group at the Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Media Technology IDMT has been working on people's individual sound preferences. The focus is on intelligent hearing solutions for special acoustic challenges. For a recent study¹, the researchers focused on driving noises that influence the musical experience while driving. They investigated how preferences for playback volume and sound balance differ in several ambient noises while driving. 18 test subjects with normal hearing aged between 23 and 51 years were asked to select their individually preferred settings when listening to music in a quiet environment. In addition, they were asked to repeat the task with nine different driving sounds played in random order. These tests were carried out twice on different days with each participant. The YourSound audio software developed at the Oldenburg branch of the institute was used, which enables personal sound settings to be made very efficiently and playfully using music samples.
Sound preferences change with the noise level
The researchers' observations confirm that, on average, the music is set louder and with more bass by the test subjects when loud driving noise is present. Some modern infotainment systems also take this approach automatically as soon as it gets louder in the vehicle due to rolling and wind noise. However, the researchers were able to recognize that the adjusted levels and balances differed significantly from person to person. "These personal sound settings remained very stable even when the study was repeated on another day. A personal sound preference was therefore clearly recognizable for all participants,” explains PD Dr. Jan Rennies-Hochmuth, Head of the Personalized Hearing Systems Group at the Fraunhofer IDMT in Oldenburg.
The study was therefore particularly interested in the sound settings that were made during the playback of the various driving sounds. Despite considerable level and spectral differences, the preferences changed only slightly in the different driving sounds. However, they differed greatly between the individual test subjects and also showed significant deviations from the adjustments without background noise.
The researchers have thus demonstrated that an individual adjustment of sound preferences can be beneficial, and that ambient noise should also be taken into account – which is an important result, especially for improving audio playback in cars.
Individual sound adjustments in two steps
For practical application, a number of findings can be drawn from the results of the study: People have individual hearing preferences in both quiet and noisy driving scenarios. A standardized increase in volume and low frequencies in the presence of background noise cannot therefore satisfy all sound preferences. The good news is that personal sound profiles could be limited to two one-time settings – one for quiet environments and one for scenarios with driving noise.
“Infotainment systems with such simple but flexible options for adjustment can enable passengers to benefit from a significantly better listening experience in vehicles”, says Sina Buchholz, head of the study and research scientist at Fraunhofer IDMT. The researchers also see potential applications beyond the car. Once adjusted personal settings could be transferred to other devices, such as headphones or mobile speakers.
---
¹
The results of the study were published on June 17, 2024 in the article “Investigating Individual, Loudness-Dependent Equalization Preferences in Different Driving Sound Conditions” by Jan Rennies, Sina Buchholz, Andreas Volgenandt, Tobias Bruns, Christian Rollwage and Jens-E. Appell published on the website of the Audio Engineering Society (https://aes2.org/publications/elibrary-page/?id=22639).
Hearing, Speech and Audio Technology HSA at Fraunhofer IDMT
in Oldenburg
Founded in 2008 by Prof. Dr. Dr. Birger Kollmeier and Dr. Jens-E. Appell, the Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Media Technology IDMT’s Branch for Hearing, Speech and Audio Technology HSA stands for market-oriented research and development with a focus on the following areas:
- Speech and event recognition
- Sound quality and speech intelligibility
- Mobile neurotechnology and systems for networked healthcare
With in-house expertise in the development of hardware and software systems for audio system technology and signal enhancement, the employees at the Oldenburg site are responsible for transferring scientific findings into practical, customer-oriented solutions.
Through scientific cooperation, the institute is closely linked to the Carl von Ossietzky University, Jade University of Applied Sciences, and the University of Applied Sciences Emden/Leer. Fraunhofer IDMT is a partner in the »Hearing4all« cluster of excellence and in the Collaborative Research Centre »Hearing Acoustics«.
Further information on https://www.idmt.fraunhofer.de/hsa
Contact for the media:
Christian Colmer
Head of Marketing and Communication
Fraunhofer-Institute for Digital Media Technology IDMT
Oldenburg Branch for Hearing, Speech and Audio Technology HSA
Marie-Curie-Str. 2
26129 Oldenburg
Phone +49 441 2172-436
christian.colmer@idmt.fraunhofer.de
http://www.idmt.fraunhofer.de/hsa
Originalpublikation:
“Investigating Individual, Loudness-Dependent Equalization Preferences in Different Driving Sound Conditions” by Jan Rennies, Sina Buchholz, Andreas Volgenandt, Tobias Bruns, Christian Rollwage and Jens-E. Appell published on the website of the Audio Engineering Society (https://aes2.org/publications/elibrary-page/?id=22639)
Weitere Informationen:
http://www.idmt.fraunhofer.de/hsa
Ähnliche Pressemitteilungen im idw